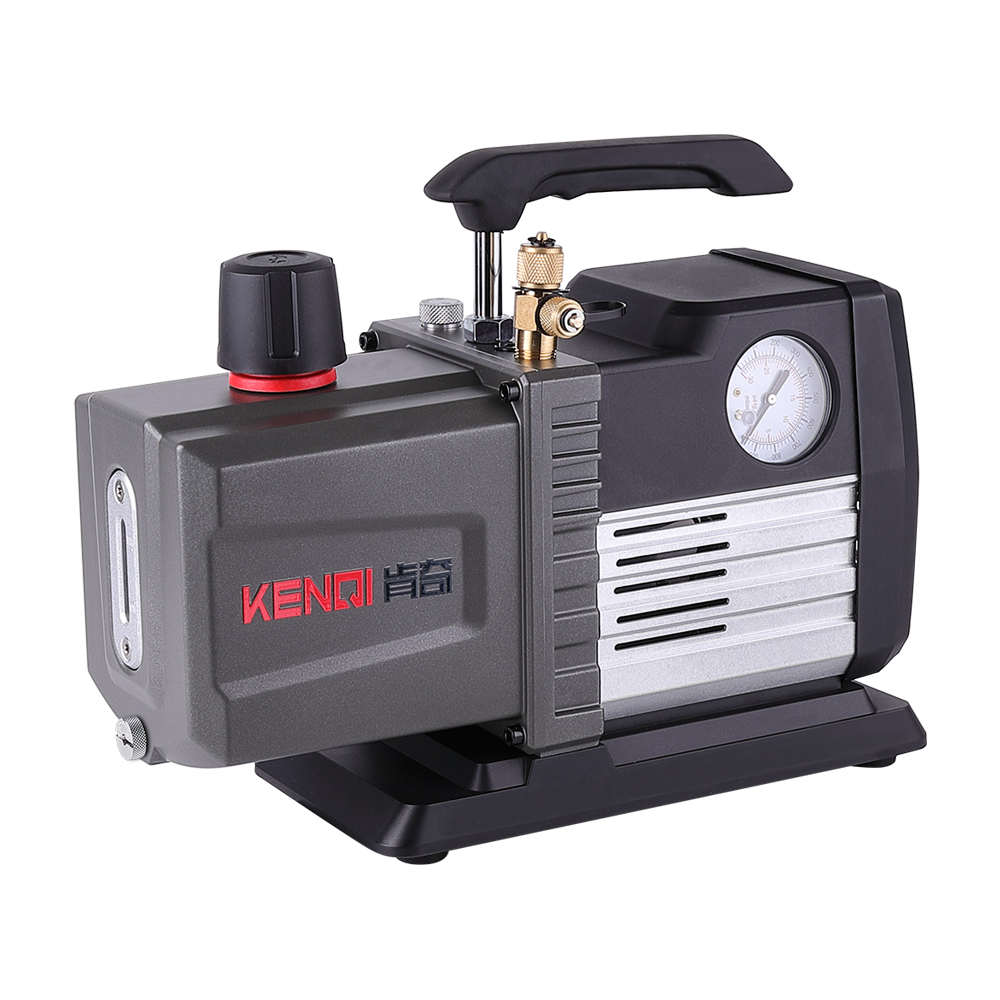
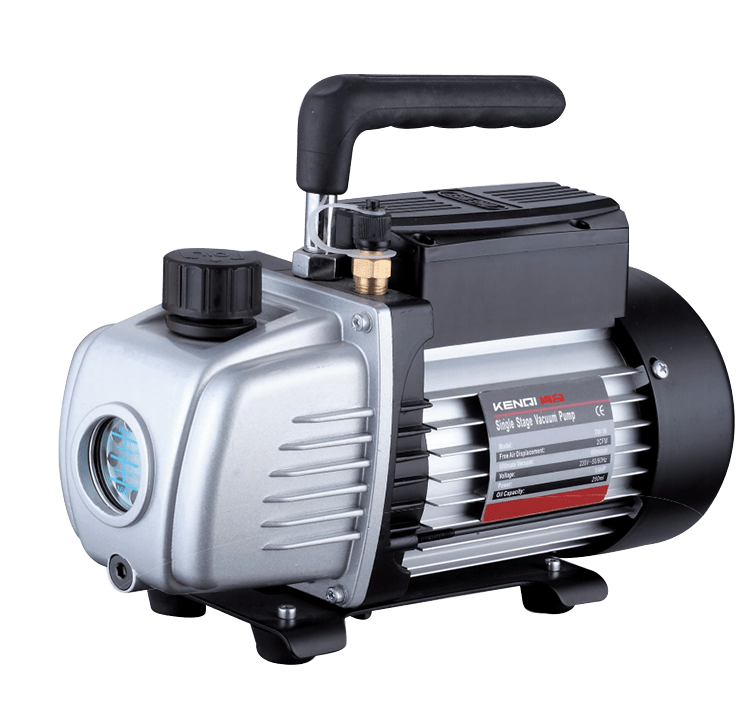
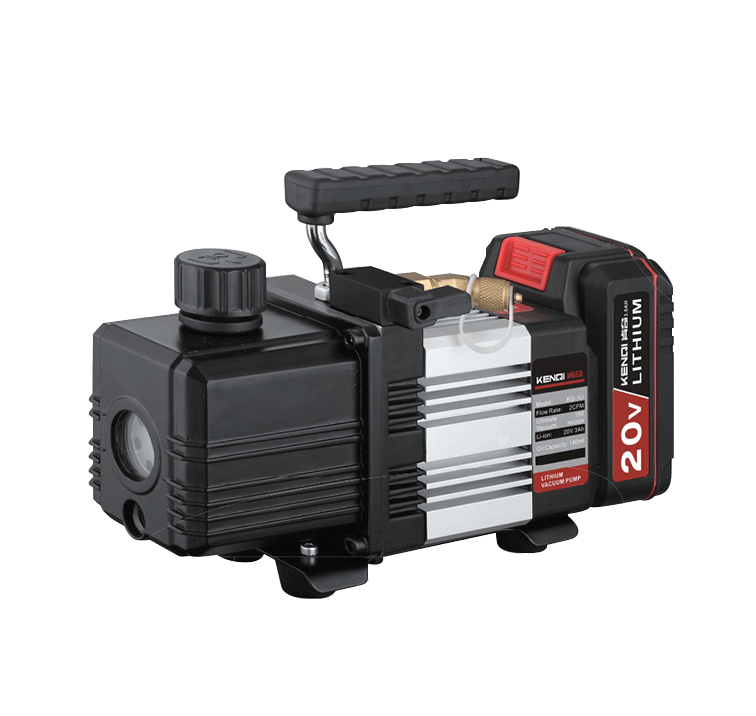
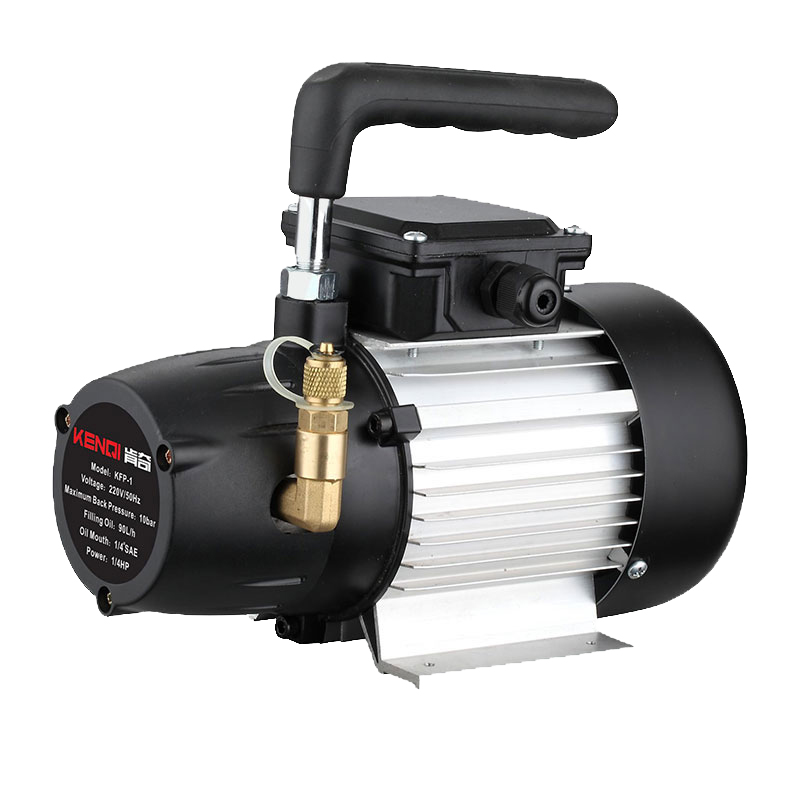
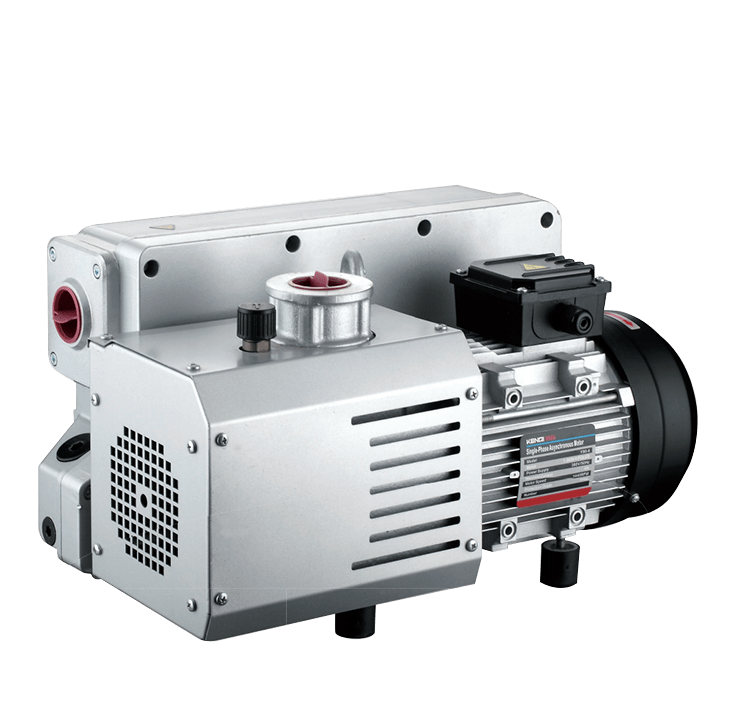
Figure 1 Vacuum Pump Component Names
A vacuum pump refers to a device or equipment that achieves a vacuum by evacuating a container using mechanical, physical, chemical, or physicochemical methods. In layman's terms, a vacuum pump is a device that employs various methods to improve, generate, and maintain a vacuum within an enclosed space.
In photocatalysis applications, vacuum pumps are used to achieve a vacuum state within the reaction system, minimizing interference from other gaseous impurities during detection. Additionally, after completing a single injection cycle in the photocatalytic apparatus, the vacuum pump must evacuate the sample loop to prepare for the next sampling operation.
1.Vacuum Pump Specifications
Pumping Speed: 360 L/min
Ultimate Pressure: 5 Pa
Power Supply: 220 V~/50 Hz
Power Consumption: 550 W
Oil Capacity: 980 mL
2.Installation of Vacuum Pump
(1) Place the vacuum pump horizontally in a dry, well-ventilated, and clean location, maintaining a clearance of >2 cm from surrounding objects and >5 cm at both ends. When installing it on equipment, ensure normal air intake at the fan cover end.
(2) Securely wrap PTFE tape around the inlet port and attach the matching nut. Insert a flexible hose into the connection, with the other end connected to the reaction system or reactor requiring vacuum.
(3) If the gas being evacuated contains significant water vapor, is excessively hot, or contains impurities such as dust, install appropriate devices like a cooler or filter on the inlet pipe to prevent affecting the normal operation of the vacuum pump.
3.Using the Vacuum Pump
(1) Before use, remove the vacuum pump's vent cap (TW-1 A/15 A/M models do not have a vent cap). Then check the oil level line to ensure the oil level inside the vacuum pump is not below the oil level line. If it is below the oil level line, promptly add vacuum pump oil (it is recommended to use vacuum pump oil of the same brand as the vacuum pump).
(2) Remove the inlet cap and connect to the reaction system or reactor requiring vacuum. Use a connection hose that is not excessively long, ensures reliable sealing, and prevents leakage.
(3) Plug in the power cord and turn on the switch to operate. If an external trigger function is available, the power switch can be turned off during operation, and the vacuum pump can be activated via the external trigger.
(4) After use, promptly unplug the vacuum pump, disconnect all tubing, and securely replace both the inlet and exhaust caps.
Note: During operation, regularly monitor the oil level window. If the vacuum pump oil becomes contaminated, cloudy, or contaminated with water or other volatile substances, it will affect the pump's ultimate vacuum value. Replace the pump oil promptly.
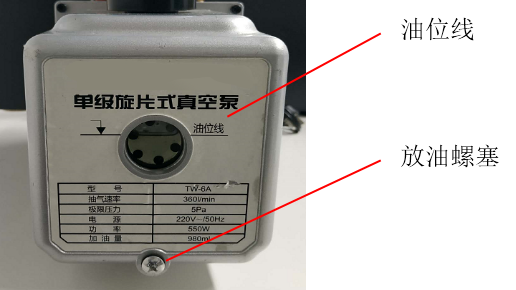
Figure 2 Vacuum Pump Inspection Window
4.Vacuum Pump Maintenance
In experiments, it is essential to maintain the vacuum pump in proper working condition to achieve the required vacuum level. Meticulous maintenance is indispensable. Below are key points for vacuum pump upkeep:
Replacing Vacuum Pump Oil:
(1) When replacing vacuum pump oil, first run the pump for 30 minutes to thin the oil before shutting it down;
(2) Disconnect the power plug and drain the old oil through the drain port;
(3) Fill the oil reservoir through the fill port to the oil level mark to flush residual oil from the chamber;
(4) Securely tighten the drain plug, reconnect the power, and run the pump for 1-2 minutes;
(5) Repeat the flushing process several times. Once cleanliness is confirmed, securely tighten the drain plug and refill the vacuum pump with clean oil through the oil inlet port to the oil level mark.
Daily Maintenance of the Vacuum Pump:
(1) Keep the vacuum pump clean to prevent debris from entering the pump.
(2) Maintain the vacuum pump's oil level. Never operate the pump without oil.
(3) Replace vacuum pump oil promptly if it shows signs of emulsification, darkening, or noticeable oil-water separation. Under normal usage, oil replacement is recommended every 2-3 months;
(4) When not in use for extended periods, cover both the inlet and exhaust ports. Store in a dry location, ensuring protection against moisture and rust.
5.Precautions for Vacuum Pumps
(1) Strictly prohibited from pumping flammable, explosive, or toxic gases;
(2) Must not pump gases that corrode metals or react chemically with pump oil;
(3) Must not pump gases containing particulate dust or large amounts of water vapor;
(4) Gas temperature must not exceed 80°C; operating environment temperature range: -5°C to 60°C;
(5) Do not use as a compressor or transfer pump;
(6) Never operate without vacuum pump oil;
(7) Do not block the exhaust port while the pump is running;
(8) When unplugging, always grasp the plug firmly—never pull by the cord. Ensure the outlet is grounded;
(9) Do not place heavy objects on the power cord or allow it to be crushed;
(10) Do not use damaged plugs or sockets;
(11) Do not insert or remove the power plug with wet hands;
(12) Do not insert or remove the power plug or press any switches in areas with gas leaks.